Macroeconomics
Fiscal Policy
MINDS ON
When you think about the Great Depression of the 1930s, you may recall that the unemployment rate was high. There were also minimal government supports available. One response was for unemployed men to ride the rails, seeking employment. One plan the Canadian government had was Relief Camps. The deplorable conditions sent the men onto the On-to-Ottawa Trek to protest.

by Wikipedia

 The Great Depression
The Great Depression
What are some possible actions the government could have/should have taken during the Depression to assist people? Explain a possible effect of your idea.
ACTION
Traditionally, economists and governments have believed that government should NOT be involved in the economy, reflecting the “laissez faire” /invisible hand philosophy of Adam Smith. During the Great Depression of the 1930s, British economist John Maynard Keynes (father of modern macroeconomics) recommended the government get involved in economic activity to solve the problem of unemployment.
Economic Thought: John Maynard Keynes
“
The political problem of mankind is to combine three things: economic efficiency, social justice and individual liberty.
~ John Maynard Keynes
“
For Government borrowing of one kind or another is nature's remedy, so to speak, for preventing business losses from being, in so severe a slump as to present one, so great as to bring production altogether to a standstill.
~ John Maynard Keynes, 1933

“
If the Treasury were to fill old bottles with banknotes, bury them at suitable depths in disused coal mines which are then filled up to the surface with town rubbish, and leave it private enterprise on well tried principles of laissez-faire to dig the notes up again (the right to do so being obtained, of course, by tendering for leases of the note-bearing territory), there need be no more unemployment and, with the help of the repercussions, the real income of the community, and its capital wealth also, would probably become a good deal greater than it actually is.
~ John Maynard Keynes, 1936
Government Budgets
When governments are preparing their annual budget, they consider revenue (from taxes) and expenditures (government spending). Their budget choices will depend on where the economy is in the business cycle, as well as their political perspective.
Budget (B) = Taxes (T) - Government spending (G)
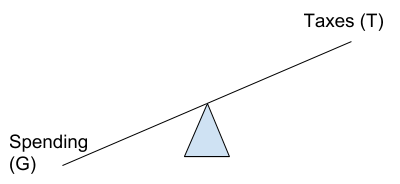
Deficit Budget
When G >T, the budget is in deficit. This is referred to as an Expansionary fiscal policy because the government is trying to expand the economy through spending.
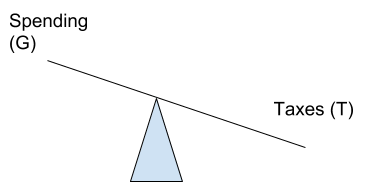
Surplus Budget
When G < T, the budget is in surplus. This is referred to as an contractionary fiscal policy because the government is trying to slow down the economy through reduced disposable income leading to less spending.
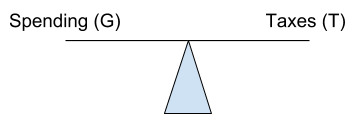
Balanced Budget
G = T
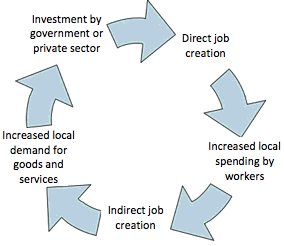
Keynes said, instead of balancing the budget every year (T=G) that the government should balance the budget over the business cycle.
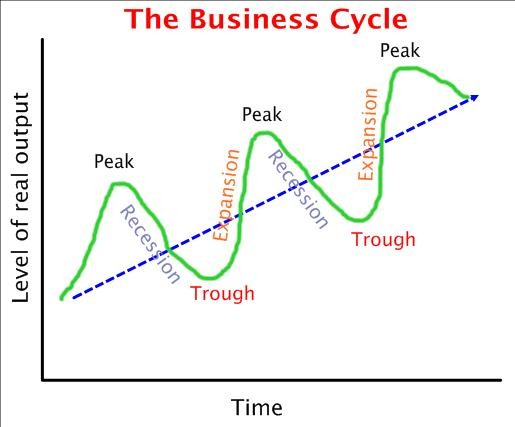
- During peak (T>G), the surplus should be kept to pay for the deficit budget.
- Thus fiscal policy advocates direct government involvement in economic activity, whereas monetary policy prefers an indirect approach.
Fiscal Policy is a response to economic problems. The two most common economic problems are unemployment and inflation. Fiscal policy would suggest the following responses.
 Fiscal Policy Responses
Fiscal Policy Responses
As you watch this video, take notes on the following:
- Expansionary and contractionary fiscal policy
- Crowding out
- Multiplier effect.
One concept that was quickly passed over was that of the Paradox of thrift. Traditionally, we have always believed that it is important to save our money, and saving is a virtue…


|
Drawback to Fiscal Policy |
Benefits of Fiscal Policy |
|---|---|
|
|
Debt vs. Deficit
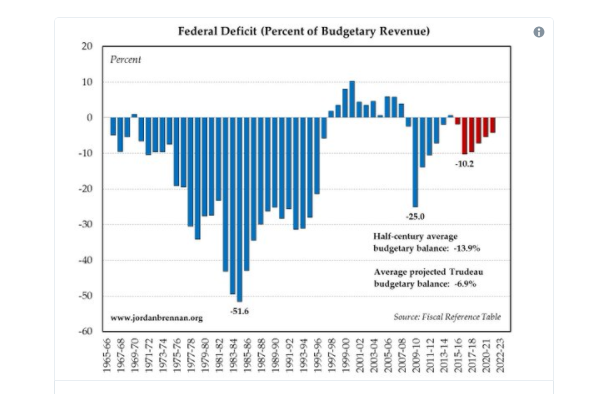
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)
 Government Deficits
Government Deficits
What is the date of this article? Go to Statistics Canada and look up Canada’s deficit and total debt as of last month. What conclusions can you make about the federal debt/deficit? Use this evidence to develop a headline and cite your sources.
Taxes
There are three levels of government in Canada and they all can levy taxes. There are different types of taxes for each level of government. In 2014, the federal government had the following balance of revenue sources.
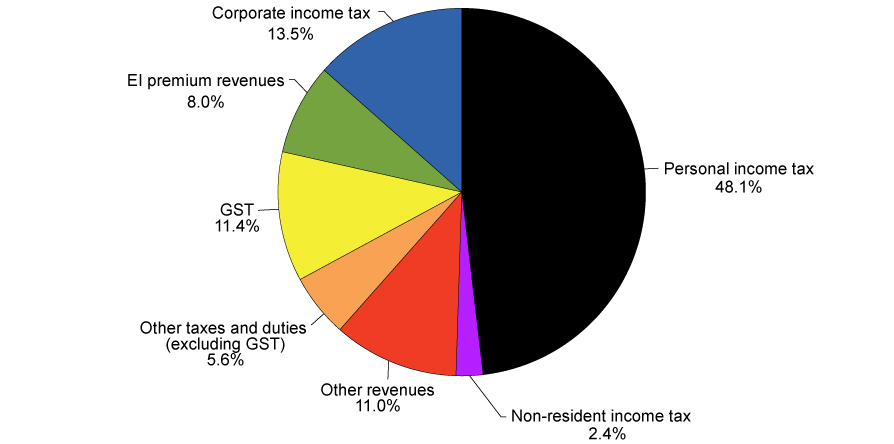
Tax Basics
A progressive tax is defined as a tax with rate increases as the payer's income increases. That is, individuals who earn high incomes have a greater proportion of their incomes taken to pay the tax. For example, income tax is a progressive tax where it changes based on income.
A regressive tax, on the other hand, is one with rate increases as the payer's income decreases. For example sales taxes are regressive because you pay the same tax on your new jeans no matter what your income is. For example, imagine two households: Gross income for Household A is $150,000, while gross income for Household B is $70,000. If the government chooses to increase the tax on hydro, that tax will have a greater impact on Household B. As a proportion of their income, Household B will be left paying more than Household A. In such a case, the increased tax on hydro would be regressive.
A proportional tax is one where everyone is required to pay an equal proportion of their income in tax such as a flat tax. This type of tax is also highly regressive as a 10% tax, for example, represents a much heavier burden for low as compared to high income households.
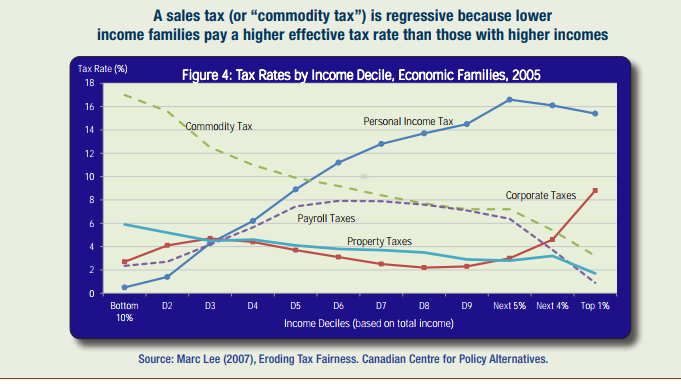
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)
When governments apply fiscal policy during an economic downturn, this means they spend more than they collect.
Deficit Budget G > T
Surplus Budget G < T
Balanced Budget G = T
When governments use fiscal policy to attempt to stimulate the economy to address unemployment, this leads to a deficit budget. Governments borrow money to pay for the increased government spending.
 Assessing Deficits
Assessing Deficits
What are the pros and cons of a deficit? Look for two different credible sources. Consider causes and effects as you consider your choices.
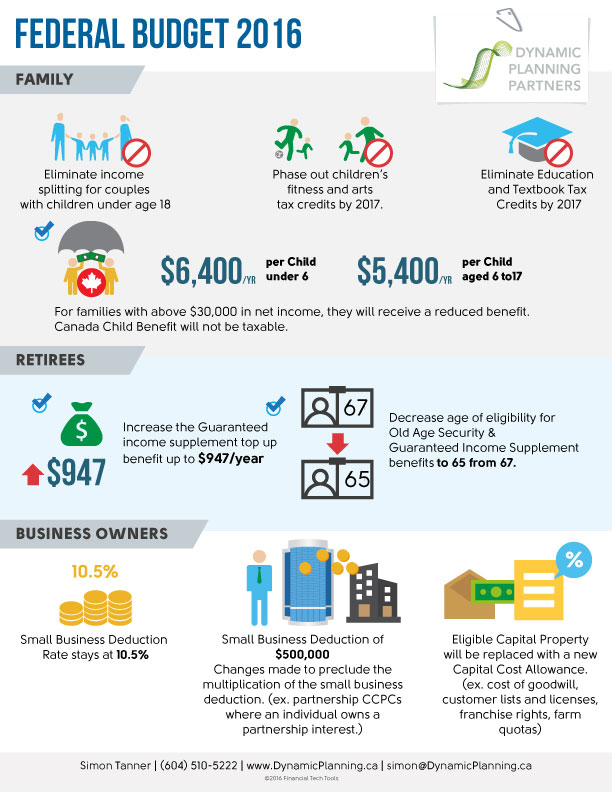
Refer to the infographic which highlights both taxing and spending changes in the federal budget; how could you use this in a blog? What element would you choose to focus on? Infographics can be used as a feature in a blog to highlight key ideas. Charts, graphs, cartoons are also effective ways to engage your audience in your message.
As you learned in Civics, each level of government has different responsibilities and spend their money on different goods and services. For example, in Hamilton in 2015, the city allocated its spending in the following way:

Fiscal Policy in Action
 Case Studies
Case Studies
As you read the case studies that follow, take notes in response to the questions.
Case Study A
Following the 2008 recession, General Motors (GM) and Chrysler in the US filed for bankruptcy. The American government provided financial support. The Canadian governments (Ontario and Canada) provided financial support as well. There are economic and political arguments for and against these actions. Read the sources that follow and determine:
- The causes and effect of the government actions (e.g., budget, debt, deficit).
- The different economic perspectives that influenced the decisions.
- What was the impact on stability and variability?
- Did the Canadian and Ontario governments make the correct decision, from an economic perspective?
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)
Case Study B
“Why might the federal government consider raising Employment Insurance (EI) premiums? How might such a policy affect firms and workers?”
Employment insurance is an automatic stabilizer that can be used to help the unemployed during an economic downturn. As you read determine:
- The causes and effects of the government action (e.g., budget, debt, deficit).
- The different economic perspectives that influenced the decisions.
- What was the impact on stability and variability?
- What alternative economic choices did the government have?
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)

Case Study C
The housing prices in several major cities and their surrounding areas have been rapidly increasing. This has meant that many people are unable to buy a home. This is causing a generational divide as older Baby Boomers have lots of equity in their very expensive homes while MIllenials are unable to pursue that same dream of home ownership. Read the sources that follow and determine:
- The causes and effects of the government actions (e.g., consumer spending, housing markets etc.)
- The different economic perspectives that influenced the decisions.
- What was the impact on stability and variability?
- What impact might government requirements regarding down payments have on potential homeowners?
- Did the Canadian and Ontario governments make the correct decision, from an economic perspective?
If you want to view any links in this pdf, right click and select "Open Link in New Tab" to avoid leaving this page. (View the original article.)
CONSOLIDATION
 Fiscal Policy Cartoon
Fiscal Policy Cartoon
Find a cartoon related to taxes, government spending or government deficit/debt published within the past 3 months.
 T or
T or  G or both?
G or both?