MFM2P
Unit 5: Culminating Activity
Activity 1: Celebration
Before you begin your final task in the course, reflect on the different relationships and their representations that you have studied. With graphs, equations, tables of values, pictorial and verbal representations all available to you, you can select different ways to solve problems.
With linear relations, you discussed the key features, slope and the y-intercept; you determined the equation of a linear relation using different information and were able to write the equation in different forms.
You found a point of intersection of two linear relations when the two lines had different slopes. You used different algebraic methods and recognized the limitations of using a graphical solution.
You learned about the key features of a quadratic relation and can identify the features using the standard and factored form of the equations. The algebraic skills of expanding and factoring gave you access to rewriting one equation in an alternate form.
Working with similar triangles, you learned about the primary trigonometric ratios and their use in solving problems involving sides or angles of right triangles. Along with the Pythagorean theorem, you now have additional tools to use when solving problems.
Measurement formulas and conversions are commonly used in our daily lives as we create the structures that surround us and figure out what materials are needed for those structures.
You have documented the different relationships in The Important Book. You can use your document as you complete the activity.
Consider all that you have learned and how you have been applying the seven mathematical processes. You recorded your awareness and use of the seven mathematical processes as you completed the activities. Once you complete your documentation in this activity, you will share a reflection with your teacher about your strengths and weaknesses with the processes.
 Mathematical Processes
Mathematical Processes
In this activity, the Mathematical Processes Problem Solving and Communicating are the focus.
Download and open U5 Mathematical Processes and read the descriptions.
As you complete the activity, notice when you are thinking about your solution and how it is being presented.
Insert your record below the description of the process.
You will be completing 6 different tasks in this activity. You can download each necessary file as you come to each task, or you can download them all here:
- Task 1 - Bridge over the River Gauss
- Task 2 - Bridges in the Park
- Task 3 - Balloons in a Pyramid
- Task 4 - Hashtag to Share
- Task 5 - Glass Decision
- Task 6 - Contest for Students
As you read each task:
- Identify the information you are given.
- Think about what you need to determine.
As you make a plan:
- Consider similar problems that you have solved in the past.
- Consider different strategies that could be used to solve the problem (or parts of the problem).
- Select a strategy or a combination of strategies.
As you carry out your plan:
- Use your chosen strategy.
- Do all necessary calculations.
- Monitor your success in completing the task.
- If another way to approach the problem comes to mind while you are working on the problem, make a record of it on your plan.
- Revise your work as needed.
As you look back at the solution:
- Make your recommendation, if required.
- Review your method; did you think of another way to approach the problem? Did you record it?
- Communicate your final answer
Submit each task to the dropbox. Use the checklist to track your work.
You have been building the green space in the fictitious town of Mathville and are planning a celebration for the 75th anniversary of their fall fair. It is almost time for the celebration. Before the celebration, there are a few remaining issues that need to be be resolved.
 Task 1 - Bridge over the River Gauss
Task 1 - Bridge over the River Gauss
A new bridge was built to the north of the park over the Gauss River. The bridge is for pedestrians and cyclists only. This type of bridge is called a cable stayed bridge.
Each section of the bridge in Mathville has a central tower that is 30 m high. The support cables extend from the top of the tower to different places alongside the bridge surface.
Download and open the Task 1 document.
Determine the length of the three support cables shown on the right side of the tower. Round answers to 1 decimal. Determine the angle that each support cable shown on the right side makes with the bridge surface. Round to the nearest degree.
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Task 2 - Bridges in the Park
Task 2 - Bridges in the Park
Additional picnic pyramids are being constructed in the northeast corner of the park. Bridges are being built across the small stream to allow people to access the structures.
The design of one bridge includes a parabolic arch, a horizontal handrail and vertical rods. The parabolic arch is defined by the equation,
y = - 0.1875x2 + 0.5625x + 0.328125
where x is the horizontal distance from one end of the bridge in metres and y is the height of the arch in metres. The arch spans the stream and is anchored to the land 0.5 m beyond the edge of the stream on each side.
Download and open the Task 2 document.
1. Determine the height of the handrail above the bridge surface.
2. Determine the width of the stream.
3. What is the height of the arch at the edge of the stream? Round to 2 decimal places. This image shows the placement of vertical rods between the underside of the arch and the bridge surface.
4. Draw the x-axis and the y-axis on the grid in Task 2. Add the scale to the axes.
5. Determine the lengths of two rods that are of different length. Give their position on the graph along with the height. Show or explain how you determined the length of the rod.
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Task 3 - Balloons in a Pyramid
Task 3 - Balloons in a Pyramid
As you complete this task, you will be asked to outline your plan before beginning any calculations. As you read the scenario, think about the information that you are given and what you will need to calculate.
For the anniversary celebration, there will be helium-filled balloons for the children. They have purchased spherical balloons that have a 9 in. diameter. When filled with helium, the balloons should continue to fly for most of the day.
Part 1: The committee estimates that they will need 1 500 balloons. They plan to purchase the cylinders of helium and fill the balloons themselves. They have two choices of cylinders:
- a medium cylinder which contains 80 cu. ft. of helium
- a large cylinder which contains 100 cu. ft. of helium
Download and complete the Task 3 document.
The committee does not want to purchase too much extra helium, but they need to have enough to fill all 1500 balloons.
- How many balloons can be filled using a medium cylinder?
- How many balloons can be filled using a large cylinder?
- How much helium is needed to fill all the balloons?
- Advise the committee of which cylinder(s) to purchase and how many of each they should order.
Part 2: The pathways in the park will be lined with
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Task 4 - Hashtag to Share
Task 4 - Hashtag to Share
At the end of the aerobatics show, the committee wants the attendees to share their comments. They will have 5 planes advertise the hashtag for making comments on the park and the 75th celebration.
Four planes will create the hash sign with smoke trails (#) and the fifth plane will drag the banner with Mathville at the end for the hashtag: #Mathville.

Download and open the Task 4 document.
The pilots have determined the following equations for the linear relations representing their smoke trails.
Equations: x is on the horizontal axis and y is on the vertical axis.
a. 2x - y - 12 = 0
b. x + 5y - 39 = 0
c. 2x - y - 1 = 0
d. y = -1/5 x + 3.4
Algebraically, determine the four points of intersection, using elimination and/or substitution. On the graph, write the correct equation on each line and label each point of intersection. Use the x and y coordinates of the ordered pairs to identify the position of the axes. Draw the axes and label the axis with values.
Direction of Flight: When pilots are following a line of flight, they are flying at an angle relative to north, and this angle is called a bearing.
The pilots know the intersection points of the flight paths and need to determine the line of flight, or bearing, for each plane. They have chosen to create the hash mark (#) with each plane flying in a different direction.
Their direction of flight is indicated by the arrow at the end of the line.
Determine the direction of flight for each plane.
- Draw the x- and y-axes on the grid. Add the scale that you determined in the previous section.
- For each flight path, determine the number of degrees relative to north, now that the arrow has been rotated.
- In your solution, be sure to communicate what triangles you created at the intersection points to solve for the angle measures by drawing them in on the grid. Round angles to nearest tenth of a degree.
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Task 5 - Glass Decision
Task 5 - Glass Decision
During the 75th anniversary celebration, different groups will be selling different snack and meal options. For consistency between the food vendors, the committee has decided to provide the glasses. They are looking at four different shapes of glasses.
Download and open the Task 5 document.
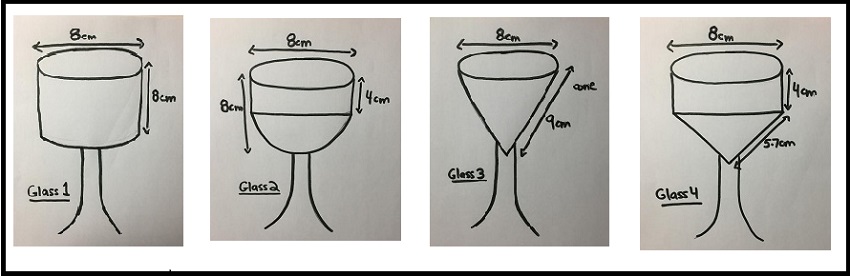
The image shows 4 glasses. Each glass has the same base but different shaped bowls.
- Glass 1 is a cylindrical bowl.
- The bowl of glass 2 is cylindrical at the top and a hemisphere at the bottom.
- Glass 3 has a conical bowl.
- The bowl of glass 4 is cylindrical at the top and conical at the bottom.
What is the maximum volume that each glass can hold if the glass is filled to 1 cm from the top of the glass? Show all your calculations. Explain your reasoning.
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Task 6 - Contest for Students
Task 6 - Contest for Students
Every year at the fair there is a contest for the students in Mathville. This year, the Grade 10 contest involves quadratic and linear expressions. The sixteen game pieces have 2, 3 or 4 expressions along the edges. There are 24 sets of equivalent expressions.
Download and open the Task 6 document.
To solve the puzzle, you need to match the multiplication of 2 linear expressions with a quadratic expression along the edge of another card.
Note:
- Matches are only along the inside edges.
- Outside borders may have an expression or be blank.
- Pieces with a blank edge are border pieces.
Move and/or rotate the individual game pieces to match the 24 sets of equivalent expressions. You can either work online or you can print the puzzle and cut out the squares. When you have matched all the linear pairs with their quadratic product, cut and paste the game pieces into their correct spots. There is an empty table on page 2 of the document to place the game pieces. Save the document. Algebra tiles, either in your class or online, may be used.
Submit your work to your teacher when complete.
 Mathematical Processes
Mathematical Processes
Complete your entry for the Mathematical Processes Problem Solving and Communicating in the document U5 Mathematical Processes.
Save to your Portfolio.
 Mathematical Processes Reflection
Mathematical Processes Reflection
Throughout the course, you documented your awareness and use of the seven mathematical processes as you completed the activities. You have documentation regarding the five processes, Reasoning and Proving, Reflecting, Selecting Tools and Computational Strategies, Connecting, and Representing in your entries for Units 2 and 3; in Units 4 and 5, your documentation focused on Problem Solving and Communicating.
For each process, you had a number of statements that guided you to recognize the use of the process:
- I know that I am (mathematical process) when I...
There were also Questions to ask yourself for each process. They helped you explore the process more thoroughly. Look back through your process documents from Activities 2 to 5. Consider instances where you made deep connections and others where you had questions.
Complete the following reflection Process Reflection on learning and applying the processes:
- Show two pieces of work/reflection/examples/discussions that documents how you have grown and developed your skills and awareness in one of the processes.
- Explain what these two pieces show with respect to your growth and development.
Submit your two pieces, and your explanation, to your teacher when complete.
 Learning Skills and Work Habits Reflection
Learning Skills and Work Habits Reflection
The learning skill you focused on during this culminating activity was Self-Regulation. As you saw throughout the course, self-regulation involves reflecting on your learning and identifying your strengths and areas of need.
The learning skills and work habits identified on your report card are: Responsibility, Independent Work, Collaboration, Organization, Initiative and Self-Regulation. Think about how your learning skills have developed throughout the course.
- Which of the six learning skills and work habits are your greatest strengths? What evidence do you have to support your self-evaluation?
- Which of the six learning skills and work habits are your most pressing areas for improvement? As you continue to learn in other courses and throughout your life, what are some ways that you can develop these skills?
Submit your Learning Skills and Work Habits Reflection to your teacher when complete.
Congratulations! You have completed the Grade 10 Applied Mathematics course.
 Course Survey
Course Survey
Please take a few minutes to complete this survey about your learning in this unit in relation to the content and learning goals. Your thoughtful responses will help us to make future courses better for students.