Initiating and Planning
Think and Brainstorm
The following video will help you increase your thinking power and provides tips on how to learn faster.
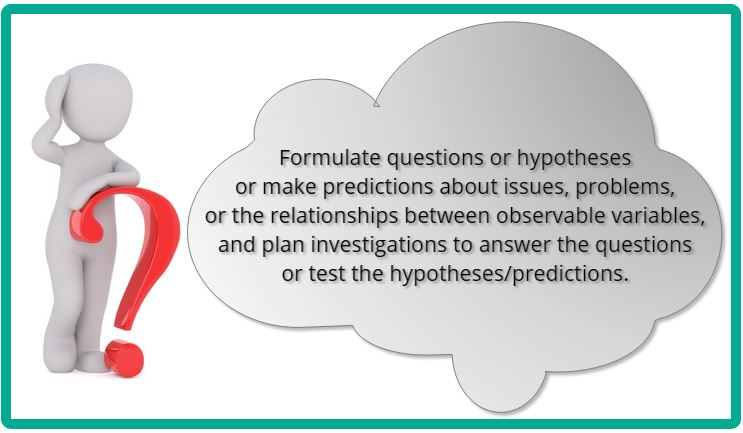
Formulate Questions
A Question Chart or Q-Chart is designed to help you formulate different levels of questions. You can download this Q-Chart if you want a copy.
The following video explores the Q-Chart and how it works.
Identify Variables
An easy way to quickly identify the variables is by thinking of the experiment as a cause-and-effect relationship.
- The cause is always the independent variable.
- The effect is the dependent variable.
- Controlled variables are factors that may affect the dependent variable.
Watch the following video on dependent and independent variables.
IdentifyVariables
Make Predictions, Develop Hypotheses
According to Google, a hypothesis is "a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation."
Predict, Explain, Observe, Explain (PEOE) is a useful tool to help you make predictions and develop a hypothesis. Here's how it works:
- Predict - You are presented with a situation and asked to predict the outcome.
- Explain - Support your predictions with reasons based on experience, previous knowledge, or research. You may use diagrams to help show your thinking. The Predict and Explain sections of the PEOE are essentially the hypothesis you would create when designing a lab.
- Observe - An activity is completed and you carefully observe what occurs and record the results.
- Explain - This second explain section is used to indicate the accuracy of your predictions. Was your prediction supported by the observations or not? You will then use additional research or new learning to explain the results that were observed.

Watch the following video to review how to make a good hypothesis based on a prediction.
Review this chart of examples of questions, hypotheses and predictions.
|
Question |
Hypothesis |
Prediction |
|---|---|---|
|
How does the size of a dog affect how much food it eats? |
Larger animals of the same species expend more energy than smaller animals of the same type. To get the energy their bodies need, the larger animals eat more food. |
If I let a 70-pound dog and a 30-pound dog eat as much food as they want, then the 70-pound dog will eat more than the 30-pound dog. |
|
Does fertilizer make a plant grow bigger? |
Plants need many types of nutrients to grow. Fertilizer adds those nutrients to the soil, thus allowing plants to grow more. |
If I add fertilizer to the soil of some tomato seedlings, but not others, then the seedlings that got fertilizer will grow taller and have more leaves than the non-fertilized ones. |
|
Does an electric motor turn faster if you increase the current? |
Electric motors work because they have electromagnets inside them, which push/pull on permanent magnets and make the motor spin. As more current flows through the motor's electromagnet, the strength of the magnetic field increases, thus turning the motor faster. |
If I increase the current supplied to an electric motor, then the RPMs (revolutions per minute) of the motor will increase. |
|
Is a classroom noisier when the teacher leaves the room? |
Teachers have rules about when to talk in the classroom. If they leave the classroom, the students feel free to break the rules and talk more, making the room nosier. |
If I measure the noise level in a classroom when a teacher is in it and when she leaves the room, then I will see that the noise level is higher when my teacher is not in my classroom. |
Science Buddies also created this checklist for evaluating a hypothesis.
|
For a Good Hypothesis, |
What Makes a Good Hypothesis? |
|---|---|
|
Yes/No |
Is the hypothesis based on information from reference materials about the topic? |
|
Yes/No |
Can at least one clear prediction be made from the hypothesis? |
|
Yes/No |
Are predictions resulting from the hypothesis testable in an experiment? |
|
Yes/No |
Does the prediction have both an independent variable (something you change) and a dependent variable (something you observe or measure)? |
Define and Clarify the Inquiry or Research Problem
The following video will help you to define your experiment clearly.
Identify and Locate Research Sources
With the Internet at your fingertips, identifying research sources beyond those suggested in this course is a couple of clicks away. Be mindful, however, to choose websites with enough details for a high school course but without too much of the unfamiliar vocabulary that you may find on university-level websites.
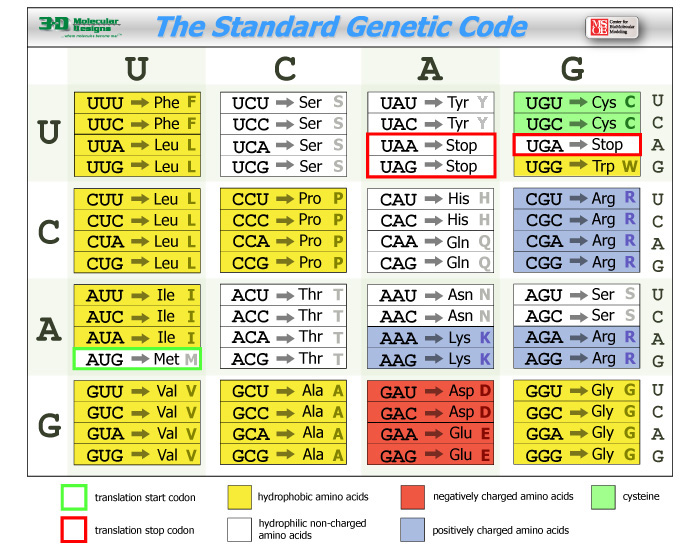
One resource that you’ll want to refer back to as you work through the second half of the course is this codon table. Click on the image to see a larger version.
Select Instruments and Materials
Building molecules using virtual molecular models takes a bit of practice to learn how the software works. Here are some instructions to help you:
1. How to build virtual molecular models.
2. How to make double bonds with the correct shape.
3. How to make ring structures.