DESCRIPTION OF INTERACTIVE
This interactive will be a simple timeline with names, dates, and images of scientists. Clicking on the scientist will open a popup and a short description of their contribution to the theories of evolution will be revealed.
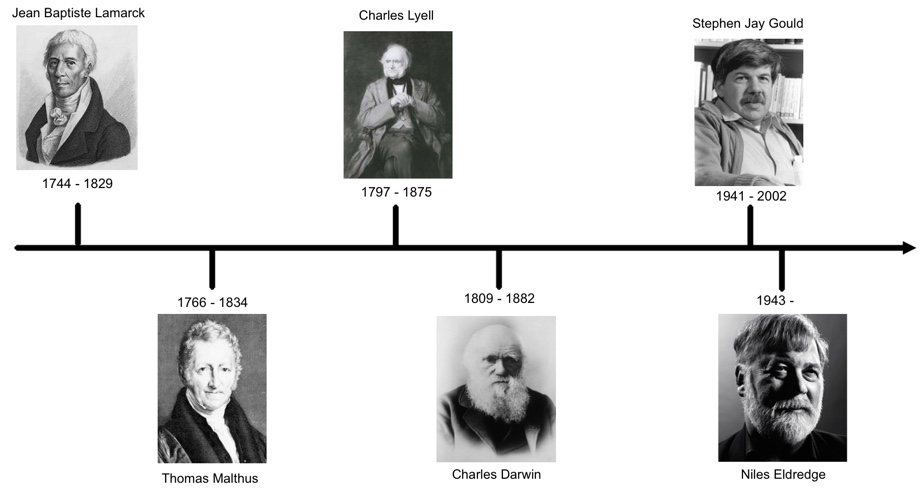
The timeline can be set up something like this:

The information that appears after clicking each image can be found below. The individual images have been included as well.
Jean Baptiste Lamarck

This French naturalist suggested that living organisms change as their environment changes. He incorrectly concluded that organisms could pass traits that they acquired during their lifetimes onto the next generation. For example, if a giraffe kept stretching its neck to reach higher leaves, the neck would eventually become longer and this longer neck would be inherited by its offspring. Although his inheritance idea was flawed, the idea of organisms changing due to environmental conditions is part of modern evolutionary theory.
Thomas Malthus

An English cleric and scholar who developed the theory of population growth due to his concerns about overpopulation and the impact it had on human happiness. His theory stated that organisms have a capacity to over reproduce, causing pressure on that population due to resource limitations. The idea is that population growth will always tend to outpace the food supply, meaning that only the better suited members of that population will survive. Malthus’ theories revolve around the idea of survival of the fittest.
Charles Lyell

A Scottish geologist who popularized the work of another scientist, James Hutton, and the theory of uniformitarianism. This theory suggests that the factors and features that shaped the Earth’s surface in the past are the same factors that shape the Earth today, and at the same rate with a similar impact. Lyell was a friend of Charles Darwin and uniformitarianism contributed to Darwin’s ideas about the processes of evolution. Although he thought there was merit in Darwin’s theories, Lyell did not publically accept evolution. Rather than evolving through generations in response to changes in the environment, Lyell instead believed that species were created to fit the current environment and would then become extinct and be replaced by a new species when that environment changed.
Charles Darwin

An English naturalist, geologist, and biologist who built upon earlier theories to explain changes he saw in various populations during his travels around the world. Darwin published some of his theories in conjunction with Alfred Russel Wallace, who independently conceived the idea of natural selection, but it was Darwin’s publication of his On the Origin of Species in 1859 and the theory of natural selection that made the theories mainstream.
Stephen Jay Gould

An American paleontologist, evolutionary biologist, and historian of science. Along with fellow scientist Niles Eldredge, Gould published the theory of punctuated equilibrium in 1972. This theory stated that evolution happens in quick bursts followed by long periods of stability with little to no change. These ideas are at odds with Darwin’s ideas that suggest that evolution is a continuous and gradual change.
Niles Eldredge

An American biologist and paleontologist who developed the theory of punctuated equilibrium with Stephen Jay Gould. He argued that if evolution is gradual as Darwin suggested, the fossil record should show a series of small developmental changes in species. Instead, the fossils indicate that many species stayed in the same stable form for long periods of time. Eldredge’s ideas include the impact that environment has on evolution, but he is a critic of the gene-centred theories of evolution held by many scientists and continues to look for alternative explanations.