Chemistry
Zooming into the Building Blocks of Matter...The Atom!
MINDS ON
Scale of the Universe
Have you ever wondered how big or small everything in our Universe truly is?
Watch this video showing the scale of the universe and explore the size of all living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) things.
 What Are You Wondering?
What Are You Wondering?
- While working through the simulation showing the size of the Universe complete the Exploration Framework to prompt your thinking and formulation of inquiry-based questions.
- Jot down your questions using the following prompt:
- I learned…this was interesting to me because....
How Small is an Atom?
Atoms are the building blocks of all materials found in our Universe - they are the smallest basic units of matter. (definition: a substance that has a mass and volume) Atoms of one type are called elements (definition: a substance that cannot be broken down into a simpler form using a chemical reaction) (found on the periodic table) and further combine to form molecules. (definition: a group of atoms chemically bonded together.)
Atoms are not visible with the naked eye - just HOW small are atoms?
Watch the video: How Small is an Atom? from TED Ed.
- While watching the video, use the Two Column Graphic Organizer to record your thoughts.
 TIP - Save Your Work
TIP - Save Your Work
- When you have completed the Two Column Graphic Organizer, SAVE the document in such a way that you can make reference to it later.
- When saving documents ensure you have named the file with a meaningful title so that you can refer back to it easily.
- Example - for the above Graphic Organizer:
- U2A3_TwoColumnNotes_HowSmallAtom_LastName.doc
 Check Your Understanding - Size of an Atom
Check Your Understanding - Size of an Atom
Once you have finished watching the video, complete the following multiple choice questions to review the content:
U2A3Quiz
ACTION
Modelling an Atom
Scientists use models to explain how an atom might look - because it is invisible to the naked eye.
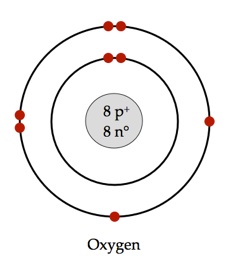
of an Oxygen atom.
Atoms are built from three (3) subatomic particles (as shown in Figure #1):
- Protons (p+): Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
- Neutrons (n): Particles found in the nucleus that have no charge (neutral).
- Electrons (dots): Negatively charged particles that surround the nucleus.
The way scientists have depicted the atom throughout history has changed based on scientific research and discovery. The Figure #2 below illustrates some of the major contributions to the current model of an atom we understand today.

Watch the video below that demonstrates how to draw a model of what the atom could look like (step-by-step), by using the Periodic Table. (definition: a table that organizes the chemical elements in an informative way.
Building an Atom - Simulation
To practice the skill of creating a Bohr-Rutherford model of an atom and to better visualize what atoms are made of, complete the Build an Atom - PhET Simulation (below).
 Building an Atom
Building an Atom
- Click the embedded simulation (below) to start the activity.
- Follow the instructions on the Build an Atom Student Guide.
- Make notes on the following:
- Describing the characteristics of sub-atomic particles that build an atom.
- Using a Bohr-Rutherford diagram to visually represent an atom.
 TIP - Save Your Work
TIP - Save Your Work
- When you have completed the Build an Atom Student Guide, SAVE the document in such a way that you can make reference to it later.
CONSOLIDATION
Atomic Structure & The Bohr-Rutherford Diagram
Remember that an atom is composed of three (3) sub-atomic particles:
- Proton (definition:A positively charged subatomic particle found in the nucleus (middle) of the atom; the number of protons in an atom are equal to the Atomic Number of the atom.)
- Neutron (definition:A subatomic particle that is neutral (no charge) and found in the nucleus (middle) of the atom; the number of neutrons in an atom are equivalent to the Mass Number minus the Atomic Number.)
- Electron (definition:A subatomic particle that has a negative charge and is found to orbit (move around) the nucleus of an atom; the number of electrons in a neutral atom are equivalent to the number of protons it has (Atomic Number))
The Periodic Table of Elements (definition:A table that organizes all chemical elements in order of their Atomic Number) is a tool that can be used to determine the components of an element’s atom - specifically scientists use the Atomic Number (definition:The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom; determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the Periodic Table (top left corner number)) and the Mass Number (definition:The total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus (middle) of the atom.)
Click on this image to open it fullsize in a new window.
Review Figure #4 (below) to familiarize yourself with important information from the Periodic Table:

Practice your skills of describing the particles that build atoms and using a Bohr-Rutherford diagram to visually represent an atom in the interactive below.
U2A3BohrDiagrams
Atoms Ants and Mars
U2A3OrderofMagnitude