Ecology
Food and Energy
MINDS ON
 Discussion - Your Most Recent Meal
Discussion - Your Most Recent Meal

For example:
This caesar salad likely contains chicken, parmesan cheese, romaine lettuce, croutons, tomato, onions and ground pepper. There isn’t a food web in the world that will include croutons or sauce! For chicken, since it is a primary consumer, you would need to find what chickens eat. Remember when you eat the chicken you are essentially eating what it ate.
Create a mind map that will trace back to where the energy in that meal came from. Place the name of the food dish at the top and work your way down. For each food, you could ask yourself, “...but where did X get the energy, oxygen and water to grow?”
Save your mind map to your Portfolio.
When saving documents ensure you have named the file with a meaningful title so you can refer back to it easily.
- Example - for the above mind map:
- U5A3_LearningSkillChecklist_TracingEnergy_LastName.doc
ACTION
If all Grade 9 Science students created a mind map of their meal, what would all of the mind maps have in common? Chances are all food you ate originated with the sun’s energy. Why? Because photosynthesis is the basis of every food web and it requires sunlight, water and carbon dioxide. Not all food comes from farms - a lot of the photosynthesis at the base of our food webs occurs in places like forests, prairies and oceans. We need these natural places all over the Earth to maintain food webs that produce the oxygen we breath and the food we eat. This need connects us! To see how the landscape has changed over the last 40 years visit this link and find where you live.
How have local ecosystems such as forests and park areas changed?
Now navigate to central Brazil; the Amazon jungle. What has happened since 1984?
Cycles in an Ecosystem
In every ecosystem there are two complementary cycles at work; photosynthesis (definition:Carbon dioxide and water react inside of the plant cell to produce oxygen and sugar) and cellular respiration.(definition:the process of a cell converting sugar and oxygen to usable energy, carbon dioxide and water.)
Photosynthesis uses the sun’s energy to transform carbon dioxide and water into sugar and oxygen.

Cellular Respiration does the opposite. People burn sugar and use oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and some water along with usable energy.

Photosynthesis and cellular respiration form a small cycle between a living animal and a plant. These are both part of several much larger cycles. One of these is called the carbon cycle.
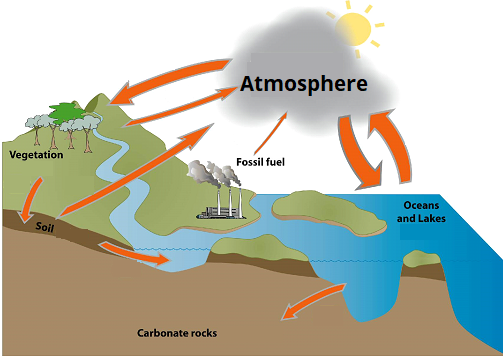
This diagram shows how photosynthesis and cellular respiration are part of a larger cycle that moves carbon throughout our ecosystem. Carbon is present in both sugar (C6H12O6, it’s big!) and carbon dioxide gas. In the final unit of the course, we will discuss the role of carbon dioxide (CO2) in warming our atmosphere. In this diagram, we see a variety of carbon ‘sinks’ or places where carbon can be stored as we attempt to limit the amount entering the atmosphere. Anything that is capable of burning (but isn’t!) is termed a carbon sink.
 Checklist
Checklist
Add the following items to the carbon cycle diagram using your favourite picture editing app or by hand (take a photo of the final product).
-
Mineral carbon, trees and fossil fuels are carbon sinks. Label them.
-
Plant respiration occurs at night (Why? No sun so plants use their stored energy!)
-
Beside the factory add an arrow → this changes atmosphere carbon dioxide levels!
-
Circle the biotic factors, place a * beside the abiotic factors